Understanding the Difference Between <a> and <Navigate> in React Router DOM
When building a React app with React Router DOM, navigation is a key part of ensuring a smooth user experience. While traditional web applications rely on the <a> tag for navigation, React provides more optimized methods like <Navigate>. But what exactly is the difference between the two, and when should you use each?
1️⃣ The <a> Tag – Standard HTML Navigation
The <a> tag is the default way of linking pages in HTML. When a user clicks an <a> tag, the browser requests the new page from the server, causing a full-page reload.
Example:
<a href="/about">Go to About</a>
Issues with <a> in React Apps:
🚨 Full-page reload — The browser fetches the new page from the server, which loses the entire app state.
🚨 Reinitializes React — Since the app reloads, all components are remounted from scratch.
✅ Use <a> only for external links where a page reload is necessary.
2️⃣ The <Navigate> Component – Programmatic Navigation
React Router DOM provides the <Navigate> component for handling internal navigation without a page refresh.
Example:
import { Navigate } from "react-router-dom"; function Home() { return <Navigate to="/dashboard" />; }
Why Use <Navigate>?
✅ No full-page reload — The app state is preserved, and only the necessary components are updated.
✅ Useful for redirects — Ideal for scenarios like automatically sending users to another page after login/logout.
✅ Works well with conditional rendering — Navigate programmatically based on state or conditions.
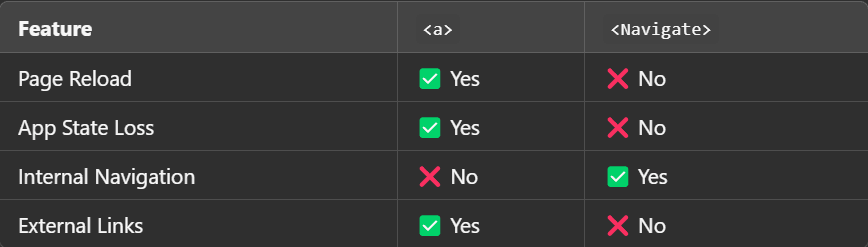
📌 Comparison: <a> vs <Navigate>
| Feature | <a> Tag | <Navigate> Component |
|---|---|---|
| Page Reload | Yes | No |
| State Preservation | No | Yes |
| Best Use Case | External Links | Internal Navigation & Redirects |
🔥 Best Practices
- Use
<Navigate>for internal navigation within a React app. - Use
<a>for external links to avoid interfering with browser behavior.
🏁 Final Thoughts
If you’re working on a React app with React Router DOM, avoid using <a> for internal navigation. Instead, leverage React's optimized solutions like <Navigate> or <Link> for a seamless, state-preserving experience.
Thanks for reading! 🚀